Programmer eyes of a medic: reduce eye strain. How to adjust the monitor for a minimum load on the eyes for Windows XP.
From constant voltage during prolonged use of the computer tired eyes. And on different types of screens (CRT, LCD, laptop screen) differently tuned (scanning frequency, number of pixels on the screen, color gamut, sharpness, contrast, brightness, etc.), the eyes behave differently. We will not talk about the fact that we need to spend less time at the computer, but we’ll dwell on how to set up the monitor so that our eyes do not get tired.
Do I need to adjust the LCD?
The average user is confident that LCD monitors themselves do not pose a health hazard. Yes, compared to monitors with a cathode ray tube, they lack X-rays, an electromagnetic field and screen flicker. The only setting for LCD monitors is setting the brightness and contrast. In fact, the monitor setting contains a wider range of indicators.
Screen refresh rate.
The value of this parameter is set by default, and rarely anyone comes to changing the factory settings. It is in vain! Changing the default setting in the monitor screen setting leads to dramatic changes.
What is the screen refresh rate? Purely intuitive, this is the flicker frequency of the screen or the number of changes in the pictures on the monitor per second. The unit of measurement is Hertz, the default value is 60 Hz (i.e., your picture will change 60 times per second). The higher the frequency, the more often the monitor changes the picture there. The human eye ceases to notice it and this is less tired.
By the way, increasing the refresh rate of the screen increases the load on the computer’s video card and the digital innards of the monitor itself. In addition, if you work with a laptop, it will automatically be followed by a reduction in its battery life.
And yet, for comfortable work and to reduce eye strain when setting up the monitor, it is better to increase the frequency.
In Windows XP ...
From scratch on your desktop, right-click to call properties. Then go to the "Options", "Advanced", "Monitor". We look at the indicator "Refresh rate of the screen."
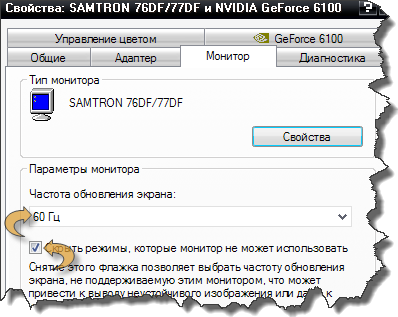
In Windows Vista, 7 ...
Right mouse button -\u003e “Screen resolution” -\u003e “Advanced settings” -\u003e “Monitor” - “Screen refresh rate”.
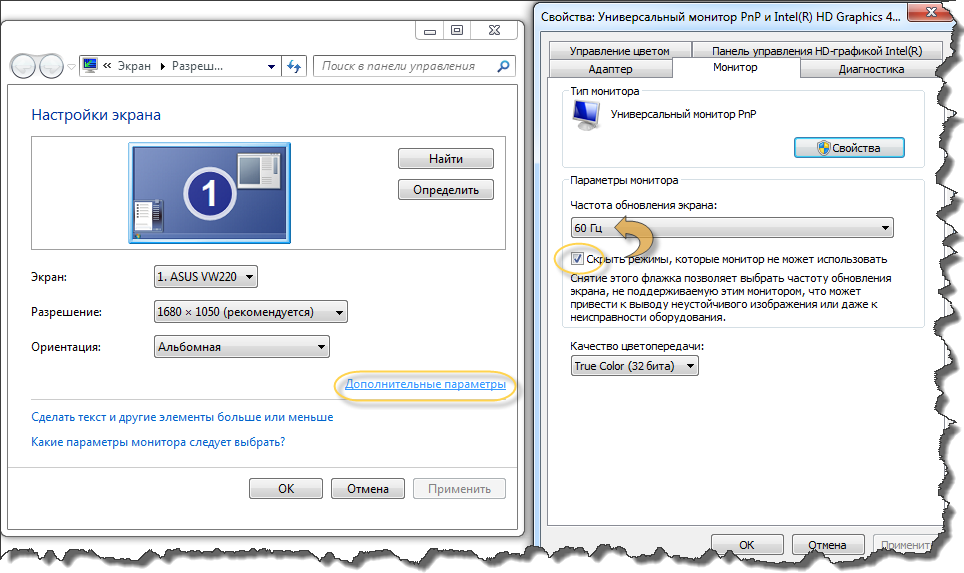
If the system gives you a choice in the drop-down list of available permissions, choose the maximum value (even if you get very small text, you can increase it by further increasing the font size). Notice the state of the option “Hide modes that the monitor cannot use.” There must be a tick, otherwise the monitor will simply not be able to show you a picture at the maximum resolution you choose.
Setting the scale of displaying pages in browsers.
A useful setting is also scaling the display of the page in the browser. The function of zooming is in all browsers. Just press the F11 key and the screen will turn. Pressing it again will return everything to its place. To change the size of the displayed text, press the CTRL key and + (plus) to increase, and to decrease CTRL and - (minus). Instead of pressing the “plus” and “minus” keys, you can use the mouse wheel. To return the original scale, use CTRL and 0 (zero).
Monitor color setting
The value of brightness and contrast, each user adjusts for themselves. It should be remembered that adjusting the colors of the monitor to high contrast will be tedious to view. Our eyes are much quicker adapting to lower brightness. As for the color range, here it is necessary to give preference to soft, warm tones, for example, green or gray. Do not chase the bright wallpaper on your desktop. Do not work in dim light. Alternately focus the eyes on far and near objects. Remember that after every 45 minutes of work at the computer you need to take five-minute breaks.
I wear glasses all my life. Astigmatism as a complication after illness in childhood with + 42 ° С. Survived.
But on the computer worked without glasses. Always intuitively set up the monitor and computer so that your eyes do not get tired.
The other day I noticed, again my eyes began to get very tired. Especially with long-term work, but before that it was not. But they gave me an LCD monitor and, given that I had to work a lot with the photo, I set it up using Adobe Gamma. This required to raise the brightness to expand the dynamic range of the monitor (elaborate dense colors). And only then I remembered why everything was normal before. But everything was normal with vision earlier because I set up the monitor of my computer to the minimum (optimal) brightness.
There are many theories, tips, SanPiN 2.2.2 / 2.4.1340-03, protective screens and special programs, all of which are dedicated to protecting the view of people working on PCs. But even when I was working in DOS, the monitors were green and had a refresh rate like regular TVs, but this problem already existed. And even then I found a way out for myself. Since then I have been working on a PC without glasses (I go and drive with glasses). Not once I watched how, in my eyes, people who had not carried out my advice for several months had to switch to glasses.
So what should you do?
The rules of workplace organization are well known:
- the monitor is at arm's length from the user (allowed 50-70 cm),
- external light should not create glare on the monitor,
- the monitor should stand at a height when the top edge is at eye level or the center of the screen at eye level,
- choose for yourself the frequency of breaks and their duration (it is recommended 1-2 times at 2 hours for 10-15 minutes),
- with a working time of more than 5 hours, take a break of about 1 hour,
- during the break, do relaxation exercises for the eyes or walk along the corridor or room,
- do not put the monitor in front of the window,
- do not place the monitor so that the light from the window falls on it,
- use special programs for training and relaxing the eyes.
Personality of view
Our eyes are very individual. As a person, they are prone to dodging work, and therefore as soon as an opportunity arises they begin to demand more comfortable conditions for themselves. And this primarily relates to the illumination of the working field. They want a comfortable light for themselves, but we, without thinking about the consequences, add light. Although too bright light is even more harmful to the eyes than its disadvantage.
If you feel eye fatigue - this is the first signal of the wrong organization of light in the workplace. And the most important aspect of the workplace organization is optimal lighting.
But, as mentioned above, our organisms and eyes are very individual. This means that each person needs individual working conditions for the illumination of the workplace, and hence the PC screen. And do not be alarmed if it seems to you that when you change the lighting in the room, your eyes feel a loss of comfort, they are right because, as will be said below, comfortable illumination or brightness of all objects in the workplace are connected.
Monitor brightness
The main requirement is to set a comfortable brightness of the monitor screen (I lower it if possible). With such brightness, the screen should not be too pale and require eye strain when reading text. But it shouldn't be too bright either. Both in the first and in the second case, the eyes get tired and even faster. And, as I do not get tired of repeating, this setting is strictly individual and the monitor with optimal tuning for one user may not be optimal for another.
Screen refresh rate
On monitors with cathode-ray tubes (CRT), the screen refresh rate is desirable maximum.
This is due to the fact that the phosphor of the points forming the image on the screen glows for a limited time, and the image unfolds in half-frames with a frequency equal to half the scanning frequency you specify. And this frequency is on the verge of the eye's response to changes in brightness, which is about 22 Hz.
(The critical frequency is about 20 Hz, but it is also individual. As the hearing of one person distinguishes sound with a maximum frequency of 18 KHz, and the other only 13 KHz (sometimes less), so the vision of different people has a different reaction to the change of light (screen refresh rate ). In Russian television, the standard sweep frequency is 50 Hz, and half-frames follow with a frequency of 25 Hz.)
With an increase in the frame rate (screen refresh rate in the monitor settings), we move away from this critical point and have a refresh rate at the screen with a frequency that guarantees the absence of flicker. The main thing that this maximum frequency supported monitor and video card.
For monitors with progressive (frame-by-frame) scanning, the refresh rate of the screen should not be a multiple of 50 Hz (the flickering frequency of lighting devices) and maximum for dynamic (games with fast motion) applications.
In a progressive scan, the entire frame is constructed by sequentially turning on the screen pixels (by line and by frame) from the first to the last. And the frequency of bypassing the screen is equal to the frame frequency. It is more than 2 times higher than the monitor screen refresh rate on a CRT. Therefore, flicker problems do not seem to exist. A high refresh rate is needed to increase the monitor's response to fast movement in the game, fast graphics (viewing rapidly changing processes). If the refresh rate of the LCD monitor is low, such scenes become blurred (lose clarity). In office applications, graphic editors, the frequency of 60 Hz is enough.
Modern LCD monitors have a high switching speed, so they are subject to recommendations similar to monitors on cathode ray tubes. (Maximum refresh rate)
Experiment with the screen refresh rate (look at the screen at different refresh rates). You will notice the frequency when exceeding which the text on the screen will begin to distort (blur, border appears or blurred). Reduce the frequency to the highest definition image and work. Eyes will be less tired.
Workplace lighting
Everything written above applies to the lighting of the workplace. The illumination of the table with the keyboard and documents should be about the same all the time and not too high. To do this, in rooms where they work with a PC, both general lighting of the room and local lighting should be combined. General lighting should be dim comfortable, with its deficiency is used as an additional - local lighting.
Now what do regulatory documents say about ambient light?
SanPiN 2.2.2 / 2.4.1340-03
Clause 7.3.
The hygienic requirements for personal computers and work organization says:
"Illumination on the surface of the table in the working paper placement area should be 300-500 lux. It is allowed to install local lighting fixtures for highlighting documents. Local illumination should not create glares on the screen surface and increase the screen illumination more than 300 lux."
SA. As you have noticed, SanPiN limits the maximum values of illumination. Practice shows you can not strive for them, given the individual properties of your body, the illumination should be optimized. And at the same time it is necessary to strive for minimum levels of illumination. In such levels, eye strain is reduced. You may not be able to change the overall illumination of the room (the light just turns off), but in any case you need to have a local lighting (desk lamp) with a regulator and an incandescent lamp (other types of lamps do not allow you to smoothly adjust their brightness over a wide range)
Clause 7.4.
Should be limited to direct brilliance from the sources of illumination, while the brightness of the luminous surfaces (windows, lamps, ceiling, etc.) that are in sight, should be no more than 200 cd / sq. m
SA. T auger restrictions apply only to the maximum, and the increased brightness leads to rapid eyestrain.
Clause 7.7.
It is necessary to limit the uneven distribution of brightness in the field of view of the user of VDT and PC, while the ratio of brightness between the working surfaces (table, monitor screen) should not exceed 3: 1 - 5: 1, and between the working surfaces (table, monitor screen) and wall surfaces and equipment - 10: 1.
SA . If SanPiN 2.2.2 / 2.4.1340-03 sets maximum values, then really normal levels should differ by no more than 30-50%. We must try not to approach the values of SanPiN, since even here p. 7.7. contradict clause 7.3. after all, 500/300 lx is not 3/1 and certainly not 5/1. If we take the normal brightness of the working surface of 100 cd / sq. m, then according to p.7.7. The brightness of the working surfaces can be up to 500 cd / sq. m, and surfaces of walls and equipment up to 1000 cd / sq.m. and the maximum is twice as much, and this is limited to 200 cd / sq. m according to clause 7.4.
From point 7.7. should the relationship between brightness monitor - table - surface walls , equipment, furniture and other objects in the working room, and even if non-real values are indicated, the SNIP and practice confirms that their brightness (from working surfaces to surrounding equipment) should not differ much.
Clause 7.14.
Pulsation coefficient (refers to the pulsations of the brightness of the lighting - SA ) should not exceed 5%, which should be ensured by the use of gas-discharge lamps in the lamps of general and local lighting with high-frequency ballasts for each type of lamp.
SA . This requires special measurements and verification of which particular lamps are installed. In addition, fluorescent lamps, like any devices with a volume discharge, are subject to external influences of magnetic and electric fields that modulate their discharge current and, accordingly, the brightness of the light.
This is all the more important since energy saving stimulates the use of fluorescent (energy-saving) lamps, therefore most of the fixtures in offices are fluorescent. The vast majority of them operate in a pulsed mode (even with electronic ballasts). As a result, there may be pulsations of light with frequencies of 50 Hz, with the operating frequency of the electronic ballast, frequencies of external electromagnetic interference (when their period is less than the afterglow time of the phosphor of the fluorescent lamp).
These pulsations of light are superimposed on each other, on the pulsations of your monitor.
I hope you know the principle of operation of the stroboscope and you will understand the consequences for your vision of these pulsations.
Luminaires using incandescent bulbs do not have pulsations (their level is many times less) due to the inertia of heated spirals, especially lamps with halogen lamps.
Therefore, I can join the advice of Konstantin Furst:
"2. The fluorescent lamps are better off cracking at once (SA - this is a joke, mercury in the lamp, do not break it!) by installing an incandescent lamp on the ceiling. You should not have a single light source in the form of, say, a desk lamp behind the monitor. If this is not avoided, then at least direct the light of the lamp to the ceiling - this will give softer lighting. Do not agree to work with a computer in complete darkness for any price. The ancient evil forces will instantly infiltrate it and do with you what they usually do with supporting characters in horror movies. "
SA. I can add fluorescent lamps, regardless of the switching circuit or the types of ballasts used, I do not recommend using. They have a harsher light, and sometimes lamps with poor quality phosphor coating come across, so you can tan under them, because they serve as a source of ultraviolet (UV) light. A sign of this is the smell of ozone, but for this to happen, the UV level must be many times higher than the allowable one. I came across a couple of times with such lamps. Measurement of the level of UV radiation in such rooms (with installed fluorescent lamps) is mandatory, but usually is not carried out anywhere.
The physics of the discharge of a luminescent lamp (a gas discharge lamp of daylight), says that the discharge current through it flows in pulses only when a certain potential difference is applied to the discharge gap. The ignition rate of the heated gas mixture is high. Such pulses of discharge current can flow even in a fluorescent lamp with a high-frequency control gear at the moments of power supply going through zero (a sinusoidal current flows in the network).
The only way to reduce the pulsation of light from fluorescent lamps is to use phosphors with a high afterglow (more than 0.04 sec). Those who used the old pulse oscilloscopes know that there are phosphors with an afterglow for up to a few seconds, only such phosphors, if my memory serves me, everything is colored.
A message flashed, probably paid by manufacturers of contact lenses:
"04/26/09, EuroNews - Spanish ophthalmologists have conducted a study on the effect of fluorescent light on eyesight.
Their conclusion.
Light fluorescent lamps are harmful to the eyes because of its rigidity, the presence of UV components in the spectrum. It was also said about the presence of pulsations (modulation of brightness) in fluorescent lamps. "
LCD monitor
... and Nokia Monitor Test
My practice shows that LCD monitors overload eyes (I feel that even more than electron-beam). In my subjective opinion because of too much brightness and not always sufficient clarity of fonts. This overloads the eyes by increasing the load on them.
To reduce the load, it is necessary to work with texts at low brightness ( i had a 21% brightness level set on my FLATRON L1918S monitor, and now LG E2240S - about 13%) or select 10% gray background of pages in editors.
There is a Nokia program Monitor Test - NTestdesigned to configure LCD monitors.
It allows you to adjust the monitor and its parameters such as "Frequency", "Phase", "Sharpness". All these parameters are configured on small vertical lines (4th test from the left, thin vertical lines) or on thin text. When setting up, you will select the most convenient test for you. But checking on thin vertical lines is necessary in any case. You may need to adjust the phase or frequency.
This setting allows you to get the maximum quality fonts.
... and ClearType
To improve the readability of fonts in operating systems Windows XP and later versions, there is a method for smoothing screen fonts Microsoft ClearType. It is designed to increase the readability of fonts when using LCD monitors. This is similar to reducing eye strain when reading text documents. In Windows Vista, it is enabled by default, and in XP it must be enabled.
To enable ClearType anti-aliasing on XP:
- right click on desktop,
- select the "Properties" item in the context menu,
- in the "Properties - Screen" dialog that opens, click on the "Appearance" tab,
- click on the "Effects" button
- check the box next to Use the following method of smoothing screen fonts,
- in the drop-down list, select "ClearType".
- then click "OK", ..... to save the selected settings.
Eye exercises
"Improvement of sight without glasses according to Bates method" Moscow 1990. Chapter 24
Eye rest
The simplest way to rest your eyes is to close them for a more or less long period of time and to imagine something pleasant in your mind. This method serves as a means of first aid, and it must be resorted to in the first place. Only very few people benefit from it.
Palming
An even greater degree of rest can be achieved if a person closes his eyes and covers them with the palms of his hands in order to completely eliminate the light. Close both eyes and cover them with the palms of the hands, with fingers crossed on the forehead. The simple elimination of the effects of light is often sufficient to achieve a significant degree of relaxation, although sometimes the tension may increase. As a rule, successful palming includes knowledge of other ways of relaxation. A simple covering of the closed eyes with the palms is useless, if at the same time the state of rest of the psyche is not reached. When you succeed in ideally making palming, you will see the field of view so black that it is impossible to remember, imagine or see something blacker. When you achieve this, your eyesight will become normal.
Turns
See for yourself that turning not only improves your eyesight, but also reduces or completely removes pain, discomfort and fatigue.
Stand with your feet apart at a distance of about a foot (about 30 cm) from each other, facing one of the walls of the room. Tearing off a little left heel from the floor, turn the shoulders, head and right at the same time until the shoulders line becomes perpendicular to the wall to which they were facing. Now, lowering the left heel to the floor and lifting the right heel from the floor, turn your body to the left. Alternate the alternate views on the right, then on the left wall, paying attention to the fact that the head and eyes move along with the shoulders. When turns are made easily, continuously, without effort and without paying any attention to the moving objects, the person will soon notice that the tension of the muscles and nerves is reduced. (Remember, however, that the shorter you can make these turns over time, the greater your progress will be.)
Motionless objects move at different speeds. Those that are almost directly in front of you will seem to be moving at an express speed and should be heavily oiled. It is very important not to make any attempt to see clearly the objects that seem to a person at the moment of turns rapidly passing by him.
SA. Exercises are given in the original source as curative, but they are simple and can be used to rest the eyes.
This is not William G. Bates!
Exercise for the muscles of the lens
For this exercise, you must use the window from which you can see a lot of prominent items at different distances. On the glass at eye level, put a small dot with clear outlines. Having stood in front of it, look out the window, there should be several contrasting objects in one line with the point, at different distances (farther than 500 m).
Standing at a distance of 50 cm in front of your point, focus your gaze first on this point, then on an object at a distance of several meters, then at a distance of 10-15 m, and so on, up to the farthest object or horizon line. When focusing on the subject, it will be clear all other fuzzy.
Repeat the exercise several times for each eye separately.
Exercises for the muscles of the eyes
The movements of the eyes are performed while the head is stationary and in one position.
- Vertical. Eye movement up (you want to see the ceiling above your head), down (floor under your feet),
- Horizontal. Without tension, move your eyes to the right to the left.
- Circular. First, clockwise, then against.
The last two exercises are no longer William G. Bates! and improve the blood supply to the eyes.
The easiest exercise
sent by the reader Olga.
You have listed good exercises, there is one more, quite simple and effective.
Within one and a half to two minutes, you need to quickly - quickly blink, and after that, close your eyes several times. From blinking increases blood flow to the eye, and closing his eyes, are brought into the tone of the eye muscles.
Vision improves noticeably and immediately!
P.S. the author
This exercise, still contributes to the washing of the cornea with a tear fluid, which improves its condition. And, last but not least, a glitter appears in the eyes.
Programs for training and relaxing eyes
Safe EU
The problem of visual fatigue and diseases associated with it in computer personnel has been officially confirmed by the World Health Organization (Geneva, 1989). In this regard, in the early 90s, the Russian firm "Sensor" (now I did not find it) developed a program that removes visual fatigue.
The methodology is based on the discovery of the English neurophysiologist F. Campbell. The scientist found an increase in visual functions when showing certain geometric images. There are specialized devices that use the so-called Campbell - the effect for therapeutic purposes in a clinical setting. The developed software tool "Safe Eyes" includes the display of certain dynamic graphic images built on the basis of the Campbell effect.
The duration of the procedure is 8-10 minutes. The systematic use of the software during breaks and (or) at the end of the work allows to increase the efficiency of the staff and to carry out the prevention of eye diseases that occur during regular work on the computer.
The program is free and works on all operating systems starting with Windows 95.
Despite this statement, when it was said on the developer’s site that it was commercial. I could not find the owner of the program in order to ask him for permission to post the program on the site. The site of the developer of the program, the company SENSOR, disappeared from the Internet. It would be good to develop a new program that will work under modern operating systems. I suspect that by their means this program will be of higher quality.
It must be admitted that the program "Safe Eyes (the program starts and runs normally under Windows Xp)" certainly deserves attention. According to our data, this is the first Russian development of this kind, designed for the mass user.
Now the Internet has a build program Safe Eyes for Windows 7, which contains a DOS - QEMU emulator. According to some data, this assembly was made by SUPERNOVA DIGITAL RESCUE. Before work read the file read.meI especially recommend to pay attention to the procedure for closing the QEMU emulator!
Going into some institutions, I still see so-called "protective screens" on the screens of monitors.
Outdated
But for those who still enjoy leave.
Safety screens do not help in protecting eyesight, they only weaken the brightness of the monitors, but at the same time they increase the brightness of the glare. You can reduce the brightness of the monitor yourself. The brightness of glare from protective screens is high due to their polished surface. Monitor screens are now all matte! The only effect from the use of screens is a faster failure of the electron-beam monitor tubes (about a third).
P.S.
I may seem to be some old-fashioned, but current trends in light sources (Economical, LED lamps) require close attention. Their use without certification of certification (with a specific indication of the level of pulsations) is unacceptable. Moreover, constant examination and measurement of the characteristics of the light flux and its pulsation are necessary.
LED lamps create a narrowly directed luminous flux, which enhances the non-uniformity of illumination of large surfaces, which is unacceptable during intensive work of view.
At the workplaces of PC operators, LED lamps should have light diffusers that create uniform illumination on the working surface (in my opinion non-uniformity should not exceed 5%). Although this condition is purely technically, it is almost impossible to fulfill precisely for these light sources.
Your opinion whether this article has helped you can send by mail, and shortly through
Literature:
- SanPiN 2.2.2 / 2.4.1340-03 Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and work organization. http://www.skonline.ru/doc/37965.html
- Tips for organizing a workplace from Konstantin Furst. http://www.vision-ua.com/patient/sovet/CVS/Anti-EyeStrain.php
- The program for training eyes Safe Eyes (to my great regret, the links given here earlier are broken, I can recommend to search for the file of this program by the file name - se.exe or by the query "Safe Eyes download" - you will find it quickly).
- The program Safe Eyes for Windows Xp can be downloaded.
- The program Safe eyes for Windows 7 you can download. Before work read the file read.me, especially I recommend to pay attention to the procedure for closing the emulator QEMU!
- Recommendations of the American Academy of Ophthalmologists for PC workers http://medicinform.net/comp/comp_vis2.htm
- Exercises for the rest of William G. Bates "Improving eyesight without glasses according to the Bates method" Moscow 1990. >>
Today, the last article in which we set up a computer monitor, so that your eyes would be less tired and sore.
If you work on a computer, then you need to configure it correctly. How to properly configure the monitor You will learn from 2 points below.
Before you set up the monitor you need to prepare the lighting in the room. The light should be bright enough, but not much, if the brightness of the light will change, then you will need to adjust the brightness of the monitor in accordance with the light in the room. But you can not work on a computer in a dark room without consecration, from such work sharpened.
1.Adjust the brightness balance of the monitor.
Find on the keyboard of your computer a button - Fn, it is usually located on the left in the front row. And the two arrows are copied and the sun is drawn, the left and right arrows. They show an increase or decrease in screen brightness.
With the key held down Fn Press the brightness keys one by one, increasing or decreasing it until the monitor brightness appears comfortable, pleasant and suitable for work.
You should not choose a very bright brightness - this will lead to visual strain on the eyes and will contribute to the incorrect display of colors.
2. Tuning frequency.
Basically, the default screen flicker on all monitors is 60Hz. The higher the frequency, the better for the eyes, they are less tired and thus the vision does not deteriorate. You need to adjust the monitor in any case or just check the frequency of your screen.
Go to the control panel STARTgo to CONTROL PANEL, choose CLEARANCE AND PERSANOLIZEDthen we go to the section SCREENfurther in SETTING THE SCREEN PARAMETERS, choose ADDITIONAL PARAMETERS, in them we select the section MONITOR.
And in the section MONITOR set the maximum frequency of the screen.
3. Adjusting the contrast of the monitor.
You also need to adjust the contrast. Contrast in the latest versions operating system Windows is configured for the convenience of the user and for his eyes because the well-adjusted contrast of the monitor removes a huge visual load from the eyes.
And in consequence, and all the possible complications with vision. Improve vision in this case will help the correct setting of the monitor and its contrast.
Where to adjust the contrast?
Find control panel button Startselect it Control Panel. Enter a calibration into the search field and then select Calibrate monitor colors. If you are asked to enter the admin password or confirm it, enter the password or provide confirmation.
In section Calibrate monitor colors select button Further, to continue. And then read the recommendations above the pictures and adjust the contrast.
That's all you now know how to set up the monitor. Only once needed set up the monitor, that would improve vision and keep it for many years.
P.S.If you constantly observe all 5 rules of how to improve your eyesight, then your eyes will be able to see everything clearly and clearly for many years, follow them and be distant.LOOK everything 5 rules how to improve vision when working on a computer.
Why are my eyes tired of the monitor? Why behind one screen eyes blush in half an hour, and after another you can work all day and not get tired? And what to do with it?
Should I look for enemies of the people among manufacturers and download the rights in service centers? Do I need to try a dozen monitors to suddenly find the one for which the eyes do not get tired?
Meanwhile, there are several aspects of the problem, and each gives its own contribution to the discomfort for vision.
1. Excessive backlight brightness and working environment
The optimal luminosity of the monitor for working with graphics is prescribed in GOST (see A. Frenkel, A. Shadrin “Colorimetric setting of monitors”, the book is free of charge and freely available).
But we will now speak not about the workplace of a professional color corrector, but about the real user environment.
The fact is that our working conditions are usually very different from what is described in GOST. Someone is sitting facing the window and is forced to unscrew the backlight to the maximum. Someone on the contrary is located with his back to the light source and is constantly struggling with glare. Some people for some reason behind the screen turned on the desk lamp and beats in the eyes (yes, I know those!).
Often these conditions cannot be changed (employer is a dumbass, for example).
But it is best to put the monitor sideways to the window (like the entire desktop, remember how the school desks stand? - the window on the left). In this case, you not only will not experience problems with brightness and glare, but most likely also do not need to constantly change the power of the backlight during the day.
Why is too bright (and, incidentally, too dim) illumination tires the eyes?
The opening of the pupil is controlled by two types of muscles (expanding sympathetic fibers that run radially, and narrowing parasympathetic, located around the circumference), which maintain the desired diameter, depending on the illumination, like the diaphragm on the camera. And it happens constantly and reflexively, without our conscious participation:
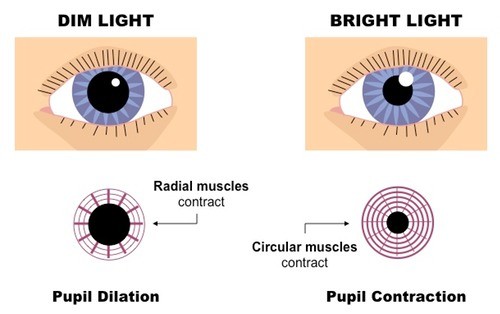
If you have to maintain long strained muscle fibers, they get tired. And from the constant constriction of the pupil eyes get tired more. At dusk or even in complete darkness, we are more comfortable to rest and relax, than in bright light. In the darkness, the eyes and the brain, as it were, pass into the stage of rest, but only as long as we do not try to force them to work in these conditions, that is, to perceive and process visual information. Then the lack of brightness will also be very tiring.
In addition, with insufficient or excessive brightness, we are still forced to keep eyelids in tension and blink too rarely or too often. Muscles can get tired of this, eyes watery or, on the contrary, mucous membrane dries.
How to properly adjust the brightness of the monitor to finish every working day with healthy eyes?
Most often, the factory setting of the backlight is made to show the monitor in all its glory in the storefront. Yes, bright, contrast, colorful. We bring it home, turn it on, go nuts and start diminishing the brightness until it feels like it is enough.
We do not take into account a single physiological factor. When going from light to dark, the adaptation time may be up to 5 minutes. That is, we reduce the backlight, and the pupil has not yet expanded adequately to this brightness, the retina has not responded, and it seems to us that it is too dark.
Many people work almost at maximum brightness, and their eyes are constantly strained to compensate for this.
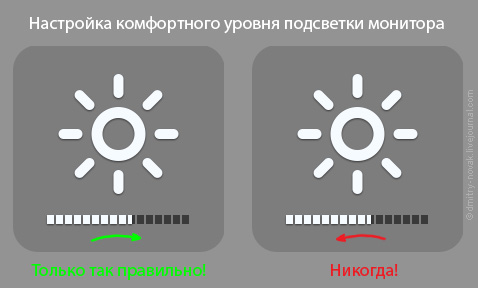
Meanwhile, it is more correct to adjust the backlight not from the maximum, but from the minimum value, gradually adding. After all, it adapts to the increase in illumination of the eyes much faster than to a decrease - this only takes 5 seconds, and not 5 minutes!
We start with a minimum and add the backlight brightness until the eyes read the information without tension, in a relaxed state. Usually, this moment of achieving a comfortable level is well felt - that was the strain on the eyes, and then it suddenly passed.
What picture to display when setting up?
Of course, this should not be a white field that completely blinds. I usually take some kind of well-known photo or even focus on good old Realcolor test wallpapers. At the same time you can see from them whether the gamma (contrast curve) is adjusted correctly.
2. Excessive contrast and microcontrast
Modern monitors have a very high contrast (that is, the difference between the darkest and the lightest simultaneously reproducible hue). This is especially true of OLED technology. But others are not far behind.
This is both good and bad for the eyes. Good, because the image is clearly visible, and bad, because within a relatively small area of the monitor, there are a number of areas with very strong contrast that do not fit the capabilities of the eye. That is, we cannot simultaneously adequately perceive the entire range of semitones. The eye does not understand what to do - either squeeze the pupil for the light part of the picture, or expand it for the dark part.
The problem is further aggravated by the fact that, at the factory setting, the shadows are usually overwhelmed, and the lights are knocked out. That is, where in the digital picture there are actually half tones, on the screen we see either solid blackness, or a white field without details.
Something like this may look like a Realcolor test wallpaper with strong contrast before calibrating the monitor:

This forces us to strain our eyes a lot, looking vainly into the shadows and light in search of information that the overly contrasting setting has eaten.
The problem is usually solved by profiling the monitor. As a result of this procedure, if we choose the Gamma 2.2 or L * setting, the semitones are more smoothly distributed over the entire range, and the details in the shadows and highlights are already much easier to read. In this case, the difference between the lightest and darkest tones usually becomes smaller, i.e. the contrast drops.

Of course, the picture of this becomes less spectacular, not so impressive, especially if we are talking about watching movies or playing games, but we make life easier for our eyes at work, it is easier to read details in shadows and highlights, such an image is easier and more comfortable to perceive. For the same reason, a paper book does not tire your eyesight as much as the text on the luminous screen of a tablet or smartphone.
LCD panels have a large microcontrast, their picture is much clearer than that of old lamp monitors (with the exception of the Trinitron technology).
On the one hand, this is good, no need to peer. On the other hand, clearly visible pixel squares are superfluous, unnatural information for the eyes. With rare exceptions, we do not want to see the cells of the screen instead of a smooth image. And in this sense, retina-displays of course facilitate the perception due to the smoothness of the contours. We are not discussing the expediency of 4K and 5K monitors; I have other material devoted to this.
3. Color temperature
Usually at the factory, the monitors adjust to their “native” color temperature, that is, no additional factors are applied to the original color values of neutral pixels, and on the white fill we get an actually pure backlight color (be it lamps or diodes). This is also due to the technical peculiarity - for LEDs and fluorescent lamps, the maximum luminous efficiency is achieved in the cold blue-green part of the spectrum.
Therefore, the factory setting usually gives a cold picture (high color temperature - 6500 K and above).
By the way, according to GOST, this temperature is recommended for preparing digital images for viewing on monitors. Again, because the factory calibration is basically this.
However, we must also take into account that 6500 K is only one of the color coordinates. At a temperature of 6500 K, the image can be both pinkish and greenish, deviating from the central heating graph vertically:
And now let's see what is better not for the car, but for our eyes.
It is believed that a typical European tends to more comfortably perceive warm lighting and color, shifted to the area of yellow shades. Evidence of this can be easily found in the world of painting and in the color rendition of the best films.
In everyday life, we consider warm light rather than cold to be cozy. If you put two table lamps with bluish and yellowish light next to it, then it will be quite clear which one is more pleasing to the eye.
This is partly due to purely national peculiarities and stereotypes of thinking, but also due to the fact that the system of “automatic white balance” in our visual apparatus (in conjunction “eye-brain”) more easily compensates for the warm shade of lighting.
The man is a day predator. Therefore, by nature, his eyes seem to be “tuned” to perceive naturally neutral sunlight. And the artificial lighting from time immemorial was yellowish - this is an open flame, and incandescent lamps, which only recently began to give way to positions of various energy-saving light sources, whose spectrum is more like pornography by an unknown artist. I was on this topic.
The paper book page is also associated with yellow paper. Enough to type in the search in Google query "book page":

You will not find here a single blue or even bluish page.
We are comfortable with what we have been accustomed to for several centuries, and not what has come into our life over the past two decades.
By the way, the second standard for setting up monitors, described in GOST and intended for preparing layouts for printing, just assumes a color temperature of 5500 K as close to the typical whiteness of the paper sheet.
Summarizing all the above, it is easy to understand that it will be most comfortable to work behind a monitor that is tuned to a low color temperature. The point of the white D55 (5500 K) is quite suitable, which is also the standard for prepress.
At first, such a calibration may seem too yellow, but the eyes will quickly get used to it and say thank you.
And although some users, whose occupation is not related to color, may not give any importance to color temperature, we must remember that it still inevitably affects visual fatigue.
4. Screen flicker
Today, the flickering monitor is not such a rare thing.
Previously, screens on cathode-ray tubes generally always had a sweep frequency that could be higher or lower, but it always was. In practice, this was expressed in the fact that the picture is drawn electronically on the screen line by line from top to bottom, but the image quickly fades away, i.e. when the beam reaches the bottom of the screen, the top lines are already fading.
With the eye it is perceived as more or less pronounced flicker, which tires.
When I used a CRT monitor, I could unmistakably distinguish scanning frequencies of 60, 75, 80, 100 hertz. Low frequency is perceived as increasing pressure on the eyes. We do not see the flicker itself, but we feel it, especially with lateral vision. If you switch the monitor from a low sweep frequency to 100 hertz at once, you can feel how the eyes relax.
Modern LCD monitors display the image in a slightly different way. Pixels on them are not extinguished, and the picture is only updated to a new one with a certain frequency, which is not perceived as flickering.
However, such a monitor may have its own trick. It's all about the backlight.
Whether it is a fluorescent lamp or LEDs, their brightness is controlled in a certain way by electronics. The easiest and cheapest way to change brightness is pulse width modulation (PWM).
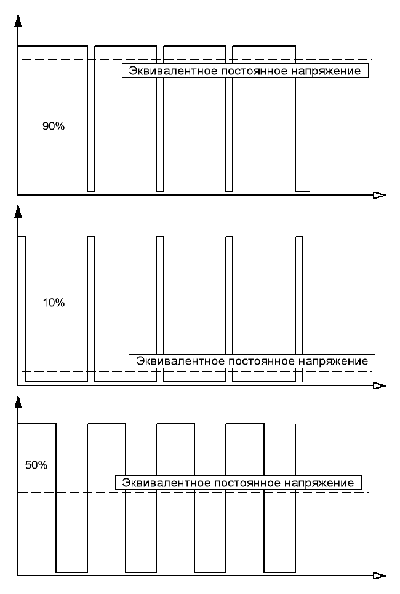
Translating a picture into a simple Russian language - the more frequent and longer pulses a lamp or a diode flickers, the brighter its glow will appear.
It is clear that at low brightness the pulses will be either more rare or shorter, which means that the effect of flicker will be more noticeable.
Usually we do not see this effect directly, although we may unconsciously feel it as a “shake” of the picture and discomfort, which contributes to fatigue during long work.
Another method of adjusting the brightness - the change in voltage. In the context of digital control of the monitor, this method is implemented somewhat more complicated. But its plus is that the image does not flicker, i.e. we always see a static picture, as if it were a slide on a viewing table.
Usually the manufacturer does not indicate that the brightness of the backlight on the monitor is regulated by PWM. But it is easy to determine the so-called “pencil test”.
We take a pencil or pen in hand and start quickly waving in front of the monitor, which displays some bright static picture.
If the screen flickers, then the smeared pencil cable will be intermittent, and if there is no flicker, then it is solid.
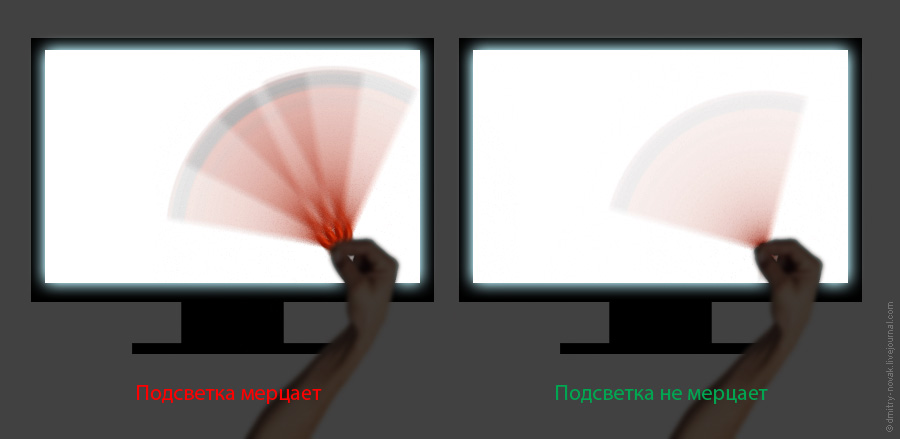

However, it is necessary to take into account such a feature that, at maximum brightness, flickering may not be at all - the pulses will be as if they are half-flat, adjacent to each other, merging into one continuous. But it is necessary to reduce the brightness, as the pulsation will inevitably come out, if it is.
It is clear that it is necessary to give preference to monitors without PWM, since, although this effect may not be noticeable directly, it will still spoil our nerves and health after prolonged use.
5. Monitor size and viewing distance
Today, when monitors with a diagonal of 26-30 ”and even more are freely available, many are trying to buy something more -“ in reserve ”. A lot is not enough, of course.
Although a large monitor allows you to see more image details with less eye strain, there are also nuances here.
Suppose we have part of the screen is occupied by a white window of a text editor or browser, and the other part displays a darker desktop.
If the monitor is small or located at an adequate distance, then it occupies only a part of the field of view, and the eye simply sticks to a certain average “exposure”. But if the screen is of considerable size (or if we put our nose on the screen), then when looking from the program window to the area with icons on the right, the eye will have to constantly adapt to the darker image and vice versa.
Naturally, this is not in vain, and we tire.
If you bought a large monitor, you should try to work behind it at a sufficient distance and, being carried away by the work, do not “fall” over time in his direction, simultaneously curling up in the pose of the question mark - after all, the comfort of the spine affects the state of the whole organism.
1. Adjust the monitor backlight from the minimum, gradually adding, and stop exactly at the moment when the information will be perceived quite clearly and without tension.
Avoid contrasting the room and light sources behind and in front of the monitor.
2. Reduce the contrast of the image, improving the readability of lights and shadows. To do this, profile your monitor on Gamma 2.2 or, better, on L *. Sometimes you can do with hardware installations.
3. Set the monitor to “warm” color temperature (about 5500 K) - this can be done both by means of the settings on the monitor itself and during the profiling process.
4. Make sure the backlight of the monitor is not flickering - with a simple “pencil test”. If there is a flicker (PWM), and at the same time the eyes get tired, then do not torture yourself, get rid of this monitor and buy a normal one.
5. Stay at an adequate distance from the screen, so that it does not occupy the entire field of your view entirely - while your eyes will be less rebuilt when you translate the view from light to dark. And watch your posture, of course.
Instruments in offices, systematic long-term work at the computer. Long focused looking at the monitor is accompanied by a decrease in the number of blinks. As a result, the cornea of the eye is not washed enough by the tear fluid, it dries up and becomes inflamed. All this leads to the development of the syndrome of "red eye" and "dry eye".
Practicing ophthalmologists have noted a significant increase in the incidence of these syndromes in recent years. After all, practically every second patient who has applied for an eye doctor’s appointment has some signs of syndromes.
To detect manifestations of eye lesions will not be difficult. They are as follows:
- foreign body sensation, sand in the eyes,
- severe tearing
- pain and burning in the eyes, worse in the wind,
- fear of bright light
- deterioration of visual performance by the end of the working day,
- fluctuation of visual acuity during the day
Prolonged visual stress can also lead to the development of tension headaches. And prolonged overstretching of the eye muscles can contribute to the development of a spasm of accommodation and the progression of myopia.
It was assumed that the replacement of monitors with an electron beam tube to a liquid crystal can significantly reduce eye strain. After all, eliminates such factors as screen flicker, complete with a strong electromagnetic field and soft X-rays.
However, in fact, the eyes continue to suffer. How can you protect them?
Many people working at the computer, sometimes even do not assume that the monitor can and should be customized. After all, the monitor with the factory settings for our eyes is a bright spotlight with poisonous colors.
Before proceeding to the settings of the computer monitor, you need to observe some conditions:
- bright light should not fall on the monitor screen
- bright light should not shine into your eyes,
- the monitor should be positioned so that you look at the screen at right angles.
Brightness
Screen refresh rate
Even at the LCD monitor, flickering may occur. It is caused by the low refresh rate of the monitor. Therefore, in the settings screen it is important to choose the optimal refresh rate.
Colour temperature
This indicator is important for a soft adaptation of the eyes when looking from the monitor screen to surrounding objects and back. Those. the image on the monitor should come close to real. You can adjust this indicator by comparing the color of ordinary white paper and white color on the monitor. The factory standard for the color temperature of a monitor screen is usually 9300K. But at this temperature, the image on the monitor is far from reality. With natural light, the image looks much bluer on the screen than it actually is. Adjust the color temperature is necessary for such lighting, in which you will work mostly. So, for example, if you work with:
- daytime natural light, then set the color temperature value to about 6500K,
- with incandescent light - 5500 - 6000K,
- under the light of fluorescent fluorescent lamps - 7200-7500K.
With such settings, the image on the monitor will be "warmer" and slightly red. You may even initially want to return everything back. But soon you will get used to it, and your eyes will be less tired.
Usually all these settings are enough for comfortable work on the computer. But this is not the limit. To make the monitor close to ideal, it can be calibrated with a special calibrator. But this is for specialists or perfectionists.
Important! Professional graphic designers cannot use the above settings on their work computer, because This can lead to poor graphics quality. Exit - work on two computers. All work that is not related to graphics, to perform on a computer with a customized monitor. So at least partially reduce the load on the eyes.
It is not a secret for anyone that the organization of a workplace is important for comfortable work. This also applies to the installation of the monitor. Here are some simple rules:
- The monitor should be located at arm's length, although perhaps 50 - 70 cm. Working on a laptop, this condition is problematic to fulfill. Therefore, to work with a laptop, you can connect a second keyboard, and place the screen at a sufficient distance.
- The center of the monitor screen or its top should be at the level of your eyes.
- The monitor should not stand in front of the window.
- Lighting (both natural and artificial) should not create glare on the screen.
- Bright light should not shine in your eyes or in the monitor.
- Workplace lighting at any time should be optimal. The best is natural light. In his absence, the overall not too bright light and the local brightness adjustable lighting (desk lamp) will be optimal. Never combine artificial and natural lighting at the same time.
- The brightness of the surfaces of the workplace and its environment should be the same.
- Do not allow pulsations of the brightness of the lighting. This mainly applies to fluorescent lamps, but it is also possible in incandescent lamps with voltage drops.
- Never work at a computer in complete darkness.
But that's not all. The organization of long-term work behind the monitor is important:
- At least 1-2 times at 2 hours, take breaks of 10-15 minutes.
- If you work at a computer for more than 5 hours, be sure to take one big break for at least 1 hour.
During breaks, do not look at the screen, try to look into the distance, get up from the table, warm up, walk along the corridor, walk through the fresh air, do exercises for the eyes.
Here are some simple exercises to help relieve fatigue, strain eye muscles and moisturize the cornea:
- Sit in a comfortable position in a chair or chair, relax and close your eyes. Sit like this for a while, remembering images that are pleasant to you. You can enhance the effect by tightly covering your eyes with your palms so that light does not penetrate through them. Try to achieve complete darkness, but do not press with your hands on the eyeballs. When performing this exercise, the retina rests, the muscles of the eye relax, the cornea is washed by the tear fluid.
- Stand near the window at a distance of half a meter from the glass. Find on the glass any roughness, a drop of paint or glue a small circle. First look at this circle. Then translate the view on the object outside the window, located at a distance of several meters. It can be a tree or a passerby. Then look at the object located far away - at a distance of 10-15 m. Then even further and so on until the last point on the horizon. Now translate the view from object to object in reverse order: from the horizon to a point on the window. And so several times. This exercise is very useful for the eye muscles - a spasm is removed from the prolonged tension of the same muscles, the lens is straightened.
- Movement of the eyeballs in the horizontal plane from left to right and vice versa, in the vertical plane from top to bottom and vice versa, rotational clockwise and counterclockwise. When performing these movements, the head must be fixed and in one position. Movements are performed slowly, smoothly, without tension. This is a good training for the oculomotor muscles.
- Blinking and squinting. First blink quickly for 30 seconds, then blink a few times. Repeat the exercise. So you moisten the cornea well.
As you can see, it takes very little time and very little self-discipline to take care of your eyes. In most cases, this is sufficient for the prevention of eye diseases caused by working at a computer.
If the symptoms of eye damage continue to bother you, especially if new symptoms appear, consult an ophthalmologist without fail. It is possible that under the guise of "eye monitor" syndrome hides a serious disease.
Lily SAVKO
